Recuperation of heat – a technology that enables retail businesses to save money
 25.06.2025
25.06.2025 
In modern retail, as in any business, savings are important. Due to rising energy prices, store owners are actively looking for ways to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
One of the most promising solutions is the recovery of heat generated by refrigeration equipment. This method not only saves financial resources but also helps to preserve the environment.
Utilisation of heat from refrigeration equipment
Refrigeration equipment, which is widely used in commercial establishments, generates a significant amount of excess heat during operation. Instead of releasing this heat into the atmosphere, modern technologies allow it to be utilised efficiently, contributing to energy savings and reduced operating costs.
Let’s look at two main methods of utilising heat from refrigeration equipment used in retail spaces:
- using air condensers to remove excess heat into retail spaces;
- heating water using additional heat exchangers for hot water supply (HWS) needs.
It is important to note that these heat recovery systems are supplementary and cannot be considered as the main source of heating or HWS, as the heat load is only possible when the refrigeration equipment is in operation. When the refrigeration equipment is not in operation, the heat recovery system also does not work.

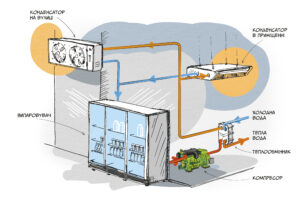
Heat recovery using air condensers
The first method of heat recovery involves the use of air recuperators (condensers), which direct excess heat from refrigeration equipment to the heating system of the sales area. This approach is highly effective in winter, when the need for heating increases, although it only serves as an auxiliary heat source.

How it works
When refrigeration equipment is running, the compressor compresses the refrigerant, which causes heat to be released in the condenser. In traditional systems, this heat is removed to the outside via external condensers. However, in heat recovery systems, air condensers are installed inside the building. The warm air generated during condensation is directed into the sales area, providing additional heating. However, if the refrigeration equipment is not operating (e.g. during night-time downtime or maintenance), there is no heat load and the system cannot provide heating.


Advantages
- Energy savings: Utilising excess heat reduces the need for additional heating sources, such as electric heaters or gas boilers.
- Indoor comfort: Even distribution of warm air provides comfortable conditions for shoppers and staff.
Limitations
- Additional nature: The system cannot be the main source of heating, as it depends on the operation of refrigeration equipment.
- Seasonal dependence: The effectiveness of this method is determined by climatic conditions and heating needs. In warm months, excess heat must be removed to the outside.
Water heating using heat exchangers
An alternative method of heat recovery involves the installation of an additional heat exchanger to heat water for domestic hot water (HWS) or other store needs.
This system is also auxiliary, as it depends on the operation of the refrigeration equipment.
How the water heating system works
Excess heat generated by the refrigeration equipment is transferred through the heat exchanger to the water supply system. In this process, the refrigerant transfers heat to the water, heating it to the required temperature. The heated water is then stored in tanks and used for domestic purposes such as:
- washing dishes
- cleaning
- heating
However, it is important to note that if the refrigeration equipment is not working, the heat exchanger cannot provide water heating.
System advantages
Versatility: Heated water can be used all year round, regardless of the season.
Cost reduction: Using recycled heat for hot water supply reduces the need for electric or gas water heaters.
Efficiency: Modern heat exchangers have a high heat transfer coefficient, which ensures maximum heat utilisation.
This approach not only saves resources but also increases the environmental efficiency of the water heating system.

Limitations
- Supplementary nature: The system cannot be the main source of HWS, as it depends on the operation of refrigeration equipment.
- High initial costs: The installation of heat exchangers and hot water storage systems requires significant investment.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to maintain
the efficiency of heat exchangers.

Comparison of methods
Both heat recovery methods have their strengths and limitations.
Air condensers are a more economical solution for additional heating during cold periods, while heat exchangers
provide versatile heat utilisation for HWS. However, both systems are auxiliary, as their operation depends on the functioning of the refrigeration equipment.
Conclusions
Heat recovery from refrigeration equipment is an effective way to improve the energy efficiency of retail outlets.
RalcoTechnic’s experienced engineers are ready to assist retailers in implementing and configuring heat recovery refrigeration systems tailored to the specific needs of each retail outlet. This will allow you to achieve a high level of energy efficiency, reduce energy costs and ensure compliance with modern environmental requirements.
To maximise efficiency, we recommend combining methods – using air condensers and heat exchangers simultaneously.
Summary
Heat recovery from refrigeration equipment in retail is a profitable investment that reduces costs, improves environmental performance and contributes to sustainable business development.
However, before deciding to implement such a system, it is important to carefully analyse your needs and possible costs.
 Sales department
Sales department 



